Rubber Silicone Molding - We Handle All Quantities
TEAM RAPID offers rubber injection molding, compression molding, and liquid silicone rubber molding to meet your specific projects.
What is Silicone Rubber Molding
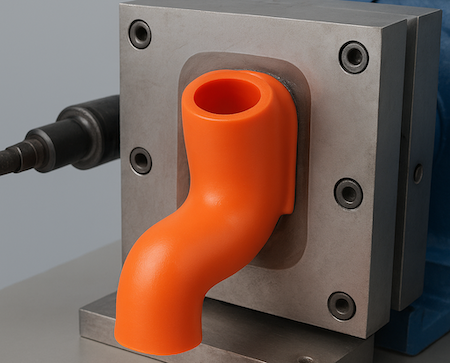
Silicone rubber molding is a precision manufacturing process that shapes silicone rubber into custom parts through heat and pressure. The process transforms liquid or solid silicone materials into durable components used in industries such as medical, automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. Unlike standard plastic molding, silicone rubber molding offers excellent flexibility, high temperature resistance, and long-term durability — making it ideal for parts that must perform reliably under extreme conditions.
Why Silicone Rubber Parts
Silicone rubber parts are trusted for their reliability, flexibility, and long-lasting performance. They can handle heat, cold, moisture, and chemicals better than most other materials, making them perfect for demanding applications.
Key Advantages
-
Wide temperature range:Performs well from –50°C to +230°C.
-
Excellent durability:Resists weathering, UV light, and aging.
-
Flexible and strong:Retains elasticity even after repeated use.
-
Safe and clean:Biocompatible, non-toxic, and odorless — ideal for medical and food-grade products.
-
Design freedom:Easily molded into complex shapes for custom applications.
Common Silicone Rubber Molding Processes
Silicone rubber molding is a versatile manufacturing technique used to produce high-quality parts with exceptional flexibility, precision, and surface finish. Depending on your design, quantity, and performance requirements, different molding methods can be applied. At TEAM RAPID, we specialize in four main silicone rubber molding processes —compression molding, vacuum casting, rubber injection molding, and liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding. Each process offers unique benefits to meet your project’s technical and cost goals.
1. Compression Molding
 Compression molding is one of the most traditional and reliable ways to produce silicone rubber parts. In this method, a pre-measured piece of solid silicone (also known as a preform) is placed into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to force the material to fill the cavity. As heat and pressure are maintained, the silicone cures and takes the exact shape of the mold. After curing, the part is removed, trimmed, and inspected for quality.
Compression molding is one of the most traditional and reliable ways to produce silicone rubber parts. In this method, a pre-measured piece of solid silicone (also known as a preform) is placed into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to force the material to fill the cavity. As heat and pressure are maintained, the silicone cures and takes the exact shape of the mold. After curing, the part is removed, trimmed, and inspected for quality.
Advantages of Compression Molding:
-
Ideal for low- to medium-volume production.
-
Suitable for large parts or thick sections.
-
Cost-effective tooling with shorter lead times.
-
Can handle high-temperature silicone compounds.
Compression molding is widely used for products such as gaskets, seals, vibration dampers, and insulation components — parts that require strength and durability at a competitive cos
2. Vacuum Casting
 Vacuum casting, also known as a silicone rubber casting method, it is a rapid manufacturing process often used for prototypes and short production runs. In this method, a master model is first created (usually by 3D printing or CNC machining). Then, a silicone mold is made around the master. Once the mold is ready, liquid silicone material is poured into it under a vacuum chamber to eliminate air bubbles and ensure a flawless surface.
Vacuum casting, also known as a silicone rubber casting method, it is a rapid manufacturing process often used for prototypes and short production runs. In this method, a master model is first created (usually by 3D printing or CNC machining). Then, a silicone mold is made around the master. Once the mold is ready, liquid silicone material is poured into it under a vacuum chamber to eliminate air bubbles and ensure a flawless surface.
After curing, the part is removed from the mold, cleaned, and inspected. The same silicone mold can typically produce15–25 copies before replacement, depending on part geometry and materials used.
Advantages of Vacuum Casting:
-
Best for small-batch or prototype production.
-
Produces smooth surfaces and fine details.
-
Excellent for complex shapes or delicate designs.
-
Allows for color matching and material flexibility.
-
Faster and more affordable than injection molding for limited quantities.
Vacuum casting is ideal for functional prototypes, product validation, and pre-production testing before moving to higher-volume molding.
3.Rubber Injection Molding

Rubber injection molding is a branch of injection molding. Rubber is the primary injection molding material for this process. The commonly used rubbers include TPE, TPU, TPV, TPR, etc., which can be in different brands and hardness depending on your project requirements. This molding method is generally the same as traditional injection mold tooling. The only difference is the material -- rubber, which is soft plastic. The tooling structure can be simplified, even with no ejection system.
As a professional rubber injection mold maker, TEAM RAPID offers high-volume and low-volume rubber molding. The undercuts usually release by manual insert for the low-volume rubber molding parts. This can deeply simplify the parting lines and ejection system. The key point is how to set the parting lines skillfully to reduce flashes on rubber molded parts.
4. Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding
 Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding is the most advanced process for producing silicone parts at scale. It uses two liquid silicone components that are precisely metered, mixed, and injected into a closed mold cavity. Once injected, the material cures rapidly under heat, forming a durable, flexible, and highly consistent product. LSR injection molding is highly automated, ensuring tight tolerances and excellent repeatability, even for complex geometries or micro-sized parts.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding is the most advanced process for producing silicone parts at scale. It uses two liquid silicone components that are precisely metered, mixed, and injected into a closed mold cavity. Once injected, the material cures rapidly under heat, forming a durable, flexible, and highly consistent product. LSR injection molding is highly automated, ensuring tight tolerances and excellent repeatability, even for complex geometries or micro-sized parts.
Advantages of LSR Injection Molding:
-
Suitable for high-volume, high-precision production.
-
Offers consistent part quality and repeatability.
-
Compatible with medical-grade and food-grade silicones.
-
Supports overmolding and multi-material designs.
-
Minimal waste and short cycle times for cost efficiency.
This process is ideal for applications in medical devices, electronics, consumer goods, and automotive components where precision and reliability are critical.
Choosing the Right Silicone Rubber Molding Process
Each molding technique offers unique benefits based on part geometry, material requirements, and production goals.
| Molding Process | Description | Molding Material | Tooling Investment | Typical Tolerance | Advantages | Best For | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Molding | Pre-measured silicone rubber (HCR) is placed into a heated mold cavity and compressed until cured. | Solid silicone rubber (HCR) | Low – simple aluminum or steel tools; fast setup and economical for smaller batches. | ±0.1–0.2 mm | Low tooling cost, Simple setup, Great for thick or basic parts | Low–medium volume production | Seals, gaskets, vibration isolators, industrial pads |
| Vacuum Casting | Silicone mold made from a master model; liquid material poured under vacuum to remove bubbles. | Polyurethane resin or liquid silicone | No hard tooling required – soft molds, low cost | ±0.1–0.3 mm | Excellent for prototypes, Smooth surface finish, Very cost-effective for small runs | Prototype and short-run batches | Functional prototypes, concept models, small custom parts |
| Rubber Injection Molding | Uncured elastomer injected under pressure into heated steel mold, then cured. | TPE, TPU, TPV, and other thermoplastic elastomers | Medium–High – requires precision steel molds | ±0.1–0.2 mm | High precision, Consistent quality, Suitable for complex parts | Medium–high volume production | O-rings, automotive seals, gaskets, flexible connectors |
| LSR (Liquid Silicone Rubber) Molding | Two-part liquid silicone mixed and injected into heated mold; cures rapidly. | Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) – medical, food, industrial grades | High – advanced steel tooling and automated system | ±0.05–0.15 mm | Fast cycle time, High automation, Ideal for thin-walled or precision parts | High-volume precision production | Medical devices, baby products, wearables, overmolded assemblies |
The right molding method depends on your budget, production quantity, and performance requirements.
-
If you need cost-effective prototypes or low-volume runs, vacuum casting or compression molding are ideal.
-
For large-scale, precision production, rubber injection and LSR molding offer the best consistency and speed.
At TEAM RAPID, we provide all these processes to help you balance tooling cost, part quality, and lead time— ensuring your project runs smoothly from prototype to production.
Compression Molding – FAQs
1. Can compression molding be used for multi-colored parts?
Yes, with proper tooling and sequential material placement, multi-color silicone parts can be produced using compression molding, ideal for functional indicators or cosmetic designs.2. How does part geometry affect compression molding quality?
Parts with uniform wall thickness and simple shapes perform best. Sharp corners or deep undercuts can cause incomplete filling or stress concentrations, which TEAM RAPID can optimize during design.3. Is compression molding suitable for medium-volume production?
Yes. While primarily used for low-volume runs, compression molding scales well for medium production without major tooling changes, keeping costs competitive.
Vacuum Casting – FAQs
4. Can vacuum casting replicate fine surface details?
Absolutely. Vacuum casting produces high-fidelity replicas of master models, making it ideal for prototypes with intricate textures or small text.5. How long do vacuum-cast molds last?
Silicone molds used in vacuum casting are short-life molds, typically lasting 15–25 parts, but they are low-cost and quick to make, perfect for prototypes and low-volume runs.6. Can vacuum casting be used for functional testing?
Yes. By choosing high-performance urethane or silicone resins, vacuum cast parts can simulate mechanical properties of production parts, allowing realistic functional tests before mass production.Rubber Injection Molding – FAQs
7. Can TPE, TPU, or TPV parts be overmolded with plastics or metals?
Yes. Rubber injection molding supports overmolding onto rigid substrates, creating integrated grips, seals, or connectors in a single production step.8. How does cavity design affect injection-molded elastomer parts?
Multi-cavity molds increase productivity but require careful flow simulation and venting to avoid defects like short shots or warping. TEAM RAPID optimizes cavity layout for each design.9. What production volumes are ideal for rubber injection molding?
Rubber injection molding is best for medium-to-high volume runs, where tight tolerances and repeatability are critical, such as automotive seals, gaskets, or keypads.LSR (Liquid Silicone Rubber) Molding – FAQs
10. Can LSR parts be transparent or translucent?
Yes. LSR allows for clear or semi-transparent parts, perfect for medical devices, protective covers, or light-guiding components. Pigments and surface finish are carefully controlled.11. How does LSR molding support medical or food-grade parts?
LSR can use biocompatible, FDA-compliant silicone, which withstands autoclaving and sterilization. Ideal for medical, wearable, and baby products.12. What design considerations are important for LSR molding?
Thin walls, sharp corners, or complex geometries require optimized draft angles and wall thickness. TEAM RAPID provides DFM guidance to ensure high precision and minimal defects.
Contact TEAM RAPID for Your Silicone Rubber Molding Project
 Have a project in mind? Whether it’s a prototype, low-volume run, or high-volume production, TEAM RAPID is here to help. Our experienced engineers provide guidance on process selection, material choice, tolerances, and tooling to ensure your parts meet your quality, performance, and budget expectations.
Have a project in mind? Whether it’s a prototype, low-volume run, or high-volume production, TEAM RAPID is here to help. Our experienced engineers provide guidance on process selection, material choice, tolerances, and tooling to ensure your parts meet your quality, performance, and budget expectations.
Why Contact Us?
-
Expert advice:Choose the best molding process — compression, vacuum casting, rubber injection, or LSR — for your part.
-
Custom solutions:Material selection, overmolding, surface finish, and precision tolerances.
-
Fast response:Get a free consultation and quote tailored to your project.
Get in touch today!
Send us your3D CAD files, drawings, or specifications, along with your volume, material, and finish requirements, and our team will provide a detailed quote and production plan.
Contact Methods:
-
Email: [email protected]
-
Phone:+86 0760 88508730
-
Request a Quote:Click Here
Let TEAM RAPID turn your silicone and elastomer designs into high-quality molded parts— efficiently, reliably, and on time.