Vacuum Casting - Prototypes & Small-Volume Plastic Parts Solution
What is Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting – people also call it urethane casting. It is a rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing process that used to produce high-quality plastic parts with closely match the appearance, feel, and performance of injection-molded components. The process involves silicone mold making and liquid resin casting under vacuum, there are no steel mold investment.

How Does Vacuum Casting Process Work
Vacuum casting is a process whereby you use a vacuum environment to draw the liquid material into the silicone mold and solidified in the casting vacuum machine. This process allows you to create plastic-based complex components for your product prototypes. It is one of the best alternatives to injection molding, and with this method, you can lower the cost of production in your manufacturing process. However, the process is more suitable for low production volumes.
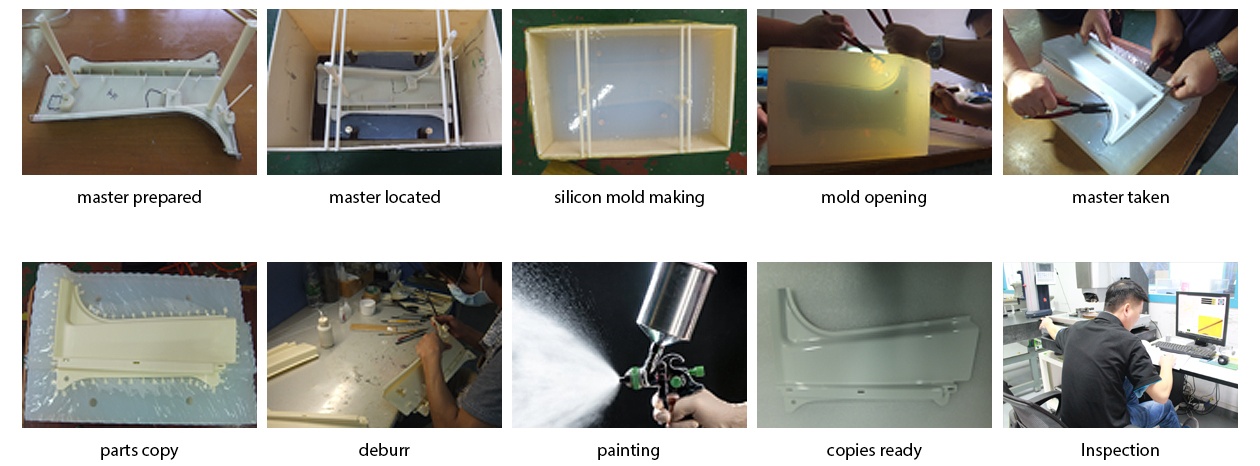
- Step 1: Prepare the master model with 3d printing services or CNC machining. Since the master patterns the casting parts, the master model must be a perfect size and cosmetic.
- Step 2: Located and firmed the master model into the proper position of a custom size wooden box.
- Step 3: Mix and pour the silicone into the box to create a silicone mold.
- Step 4: Split the silicone mold and the parting lines with a knife. This step must be processed carefully and detailed. Anything wrong usually leads to mold damage.
- Step 5: Take out the master model, maintain and store the master model well for the subsequent round silicone mold making.
- Step 6: Mix and pour the Polyurethane into the silicone mold to do the castings. Casting is under casting vacuum in a vacuum casting machine; the bubbles inside can be vacuumed out.
- Step 7: Remove the gate, overflows and flashes on the casting parts.
- Step 8: If the parts have post-finish requirements such as painting, silk printing etc., we will process them after deburring.
- Step 9: First part copied.
- Step 10: First part inspection and quality control during rapid manufacturing. If the first part is OK, then the second, the third etc. repeated under the casting vacuum machine.

Watch the Video Below to Learn More about Vacuum Casting
Benefits of Vacuum Casting in Rapid Prototyping
Vacuum casting is one of the manufacturers' most effective rapid prototyping methods. It follows the production process that is quite simple to do while helping the manufacturers to lower their production costs. There are also various other benefits of casting in rapid prototyping services, which is why many manufacturers are using this method as an alternative to injection molding. Here are the benefits:

-
Cost
Vacuum cast allows manufacturers to lower production costs while improving their output quality. Compared to the more expensive plastic injection molding service, vacuum casting can give manufacturers plenty of benefits in terms of the overall cost of production. The cost-to-value ratio is excellent with casting.
-
Precision
It’s also possible for manufacturers to produce better prototypes using the vacuum caster. The process allows prototype productions that offer more accuracy and precision, which is true to the supplied 3D design.
-
Complexity
Another beneficial aspect of the process is that it allows the manufacturers to produce the prototype designs with more complexities by vacuum casting machines. Using the liquid plastic material makes it possible for the vacuum caster to create prototypes with more complex shapes without worrying about incompatibility.
-
Material Options
There are various polyurethane plastic materials manufacturers can use in the casting process. Each polyurethane will have unique properties, allowing the manufacturers to pick the best materials based on their production applications, such as a vacuum pot for resin casting.
-
Efficiency
It is easy to produce prototypes using the casting method, and the plastic materials are easier to work with than their metal counterparts. The ease of production by vacuum casting machines will provide better efficiency for your prototype production. For manufacturers, using the casting method can help them produce more prototypes in a shorter production time while keeping their production costs within their budget.
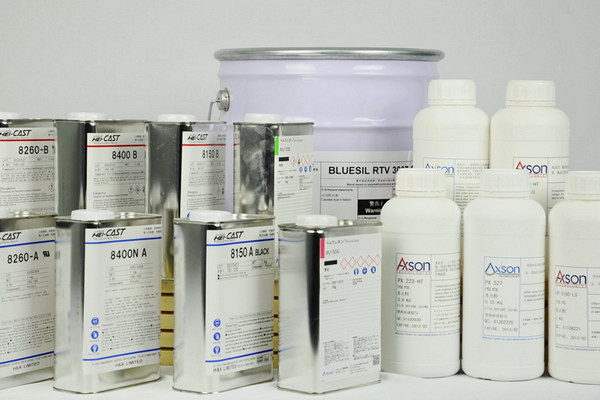
Vacuum Casting Materials at TEAM RAPID
With the development of molecular and material science, vacuum casting materials are diverse. Thermoplastics, rubbers and resins are the three major vacuum casting materials, which can emulate specific properties and characteristics, including degrees of:
 1. Physical appearance quality.
1. Physical appearance quality.
2. Surface texture/finish.
3. Transparency/translucence.
4. Rigidity.
5. Flexibility.
6. Strength.
7. Hardness.
8. Temperature resistance.
9. UV stability.
10. Color.
Commonly Used Vacuum Casting Resins at TEAM RAPID
| Vacuum Casting Material | Comments | Material Code |
| PU ABS | Flame retardant resin (UL94-V0 specification) | Hei-cast 8263 |
| PU Classic ABS | This is the classic and most popular ABS compound. | UP 4280 |
| PU Classic PP | PP resin compound - living hinges possible (typically 30 to 50 bends before breaking) | UP 5690 |
| PU PC | Transparent. Mainly stimulates filled ABS or PC. | PX 527 |
| PU PMMA(Acrylic) | UV stable. Great for glossy, clear parts. Can be tinted or colored. This is classic acrylic substitute. | UPX 5210 |
| PU Rubber | Rubber TPE resin. Variable hardness ranges from 40-85A. Can be over-molded. | UPX 5690 |
| PU Silicone | Translucent silicone that can be used as vacuum casting mold and also for vacuum casting parts. | ESSIL 296 |
Vacuum Casting Applications
Many manufacturers have been using the casting method for various applications. There are multiple uses of vacuum casting for producing prototypes and parts for different products. Here are the various usages:
-
Foods and Beverages Prototypes
Manufacturers often use plastic materials for food and beverage prototypes, such as plastic spoons, plastic forks, and other related items, which you can use once and then throw away. These prototypes use the casting method to produce, and with this method, manufacturers can speed up their production using the rapid manufacturing process.
-
Consumer Electronics
Plastic prototypes and parts are also common in consumer electronics. Plastic materials are suitable for the outer shell or housing of various electronic products. Polyurethane is the perfect material to house electrical components, as it will keep the users safe from electric currents. Manufacturers use vacuum casting to make the casing or housing for electronic products, such as smartphones, PC, laptops, and many others, in custom low-volume designs.
-
Everyday Consumer Products
There are also many consumer products you can find daily that use the vacuum casting method in their production process. These products include eyeglasses, plastic containers, toothbrushes, and many others.
Common Items Made by Vacuum Casting
| Application Category | Typical Items Produced by Vacuum Casting | Key Purpose / Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Products | Electronic housings, remote control shells, headphone casings, wearable covers, appliance knobs | Appearance validation and low-volume production with high surface quality |
| Automotive Parts | Interior trim, dashboard bezels, air vents, light covers, seals | Fit, function, and aesthetic testing before mass production |
| Industrial Equipment | Equipment housings, control panels, connectors, protective caps, fixtures | Functional testing and customized small-batch components |
| Medical & Healthcare | Medical device enclosures, diagnostic housings, instrument handles, transparent covers | High precision, biocompatible appearance models, ergonomic testing |
| Electrical & Electronics | Switch housings, connector shells, sensor covers, cable management parts | Electrical insulation and design verification |
| Transparent Parts | Clear covers, lenses, light pipes, fluid containers, inspection windows | Optical clarity and visual inspection capabilities |
| Rubber-Like Components | Seals, gaskets, O-rings, flexible covers, soft grips | Simulation of elastomeric parts without hard tooling |
| Marketing & Display Models | Show models, color samples, texture prototypes, demo parts | Visual presentation, sales, and customer approval |
| Engineering Prototypes | Fit-and-function parts, assembly test components, short-run production parts | Design validation and rapid iteration |
Vacuum Casting vs. Injection Molding
Vacuum casting is ideal for prototypes and small-volume parts need speed, flexibility, and low upfront investment, while injection molding is the best choice for high-volume, long-term production efficiency.
 When to Choose Vacuum Casting
When to Choose Vacuum Casting
-
You need high-quality prototypes or low-volume parts
-
Fast turnaround is critical
-
You want to minimize upfront tooling cost
-
Design may still change
When to Choose Injection Molding
-
You require medium to large-scale production
-
Tight tolerances and long-term consistency are essential
-
Part cost must be minimized at high volumes
-
Design is fully finalized
 When to Choose Vacuum Casting
When to Choose Vacuum Casting
Vacuum Casting vs. Injection Molding Table
| Aspect | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Low volume (typically 10–100+ parts) | Medium to high volume (thousands to millions) |
| Tooling | Silicone molds | Steel or aluminum molds |
| Tooling Cost | Low | High |
| Lead Time | Fast (days to 1–2 weeks) | Longer (weeks to months) |
| Material Options | PU resins (rigid, rubber-like, transparent) | Thermoplastics (ABS, PP, PC, Nylon, etc.) |
| Surface Finish | Excellent, close to injection-molded quality | Excellent and highly consistent |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Good, slight variation over mold life | Very high and repeatable |
| Mold Lifespan | Limited (typically 20–30 casts per mold) | Very long (hundreds of thousands to millions of cycles) |
| Design Changes | Easy and low cost | Costly and time-consuming |
| Part Cost (Per Unit) | Higher for large quantities | Very low at high volumes |
| Typical Applications | Prototypes, functional testing, short-run production | Mass production, end-use consumer products |
Contact TEAM RAPID
The application of casting parts is massive. We usually depend on the parts' function and application to suggest our customer about materials; UP4280 (ABS-like material), PX521(PC-like material), and UPX8400(Rubber-like material) are some of the most commonly used materials at TEAM RAPID. Ready for your next casting project? Contact our team at [email protected] to:
- Get a free design and process evaluation
- Receive a quick quotation based on your drawings or 3D files
- Learn how to reduce cost and lead time for your project
Upload your CAD files or drawings now, and our team will get back to you within one business day.
Vacuum Casting FAQs
Vacuum casting vs, CNC machining: Vacuum casting is just for plastic parts, and it is more cost-effective when multiple identical parts are required. CNC machining is ideal for plastic and metal parts for single or very low-quantity parts, the machining cost is 5-10 parts is significantly higher than vacuum casting.
Yes. Vacuum casting materials can simulate the mechanical behavior of common injection-molded plastics, making them suitable for snap-fit tests, assembly checks, enclosure testing, and limited functional use.
Parts produced early in the mold’s life show very high consistency. As the silicone mold ages, slight dimensional variation may occur, which is why vacuum casting is best suited for short-run production rather than long-term mass manufacturing.p>