The hot and cold runner systems in injection molding are the two most common molding systems you will need to use in your production cycles. Each one of them will have its own use within your production plan, so you need to know the differences between these runners in your injection molding process. This guide will help you understand more about the key differences you need to know between hot runner vs. cold runner injection mold.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding The injection Molding Runner Systems
- 2 The Benefits of Hot Runner vs Cold Runner
- 3 The Disadvantages of These 2 Runners
- 4 Is Hot Runner Better than Cold Runner?
- 5 Choosing between These 2 Runners in Manufacturing
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Contact Us – Get the Right Injection Mold Solution
- 8 FAQs – Hot Runner vs Cold Runner Injection Molds
- 8.1 1. Which mold type is better for prototypes or low-volume production?
- 8.2 2. When should I choose a hot runner mold?
- 8.3 3. How do hot runner and cold runner molds affect material usage?
- 8.4 4. Are hot runner molds more expensive than cold runner molds?
- 8.5 5. Can I switch from cold runner to hot runner later?
Understanding The injection Molding Runner Systems
In injection molding(including insert molding and overmolding), hot runner and cold runner have a similar system, with the only difference being that hot runner uses heat in their injection molding process. The goal for these processes remains the same, which is to deliver the plastic materials to the mold cavities, so that the injection molding process can happen.
With a hot runner injection mold, the injection mold system will use constant heat around the pipes to ensure that the plastic materials remain at their melting temperature. By maintaining the plastic materials at their melting temperature, it will be easier for the materials to go through the injection mold system into the mold cavities for further molding processes. The heat on the hot runner system can come from the internal or external heating system, depending on the preferences of the manufacturer.
Meanwhile, the cold runner injection mold doesn’t use heat to run the plastic materials through the injection molding system into the mold cavities. Instead, it uses plates to help move the plastic materials into the mold cavities for further molding processes. However, the cold runner injection mold is often slower than the hot runner counterparts because it doesn’t use heat in its injection molding system, which can affect your overall production cycles.
The Benefits of Hot Runner vs Cold Runner
Hot runner vs. cold runner, both the hot and cold runner injection molds have their own benefits. Depending on the rapid manufacturing needs and preferences, the manufacturers might use one method over the other. For instance, a hot runner might provide faster production cycles, whereas a cold runner might provide the manufacturers with the lowest cost of production.
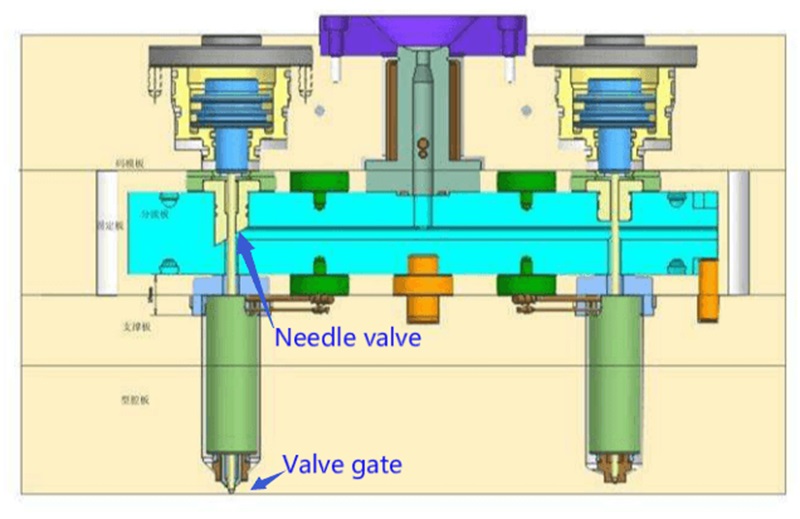
Hot Runner Injection Mold Benefits
●By using the heated injection molding system, the runner can transfer the plastic materials to the mold cavities faster, which helps speed up the overall production cycles.
●It’s most suitable for large parts production, as it is easier to direct the large plastic materials into the mold cavities using heat.
●You can fine-tune the molding process with ease, as there are various configurations you can change at any stage of production.
●The quality of the end product will be consistent and reliable, minimizing any instances of product defects during fabrication.
●Compared to the cold runner injection mold, the hot runner system produces fewer waste materials.
Cold Runner Injection Mold Benefits
●It doesn’t require expensive production and maintenance costs for the manufacturers.
●You can change the colors of the materials with ease.
●You can schedule your production time in a much simpler way.
●It’s most suitable for a wide variety of polymers and resins.
The Disadvantages of These 2 Runners
Each of the injection mold runners will have its own disadvantages too. So, you can’t just rely on one runner and expect everything will go well in your production. Every runner system, both hot and cold, can give you certain disadvantages that might affect your overall production plan or schedule.
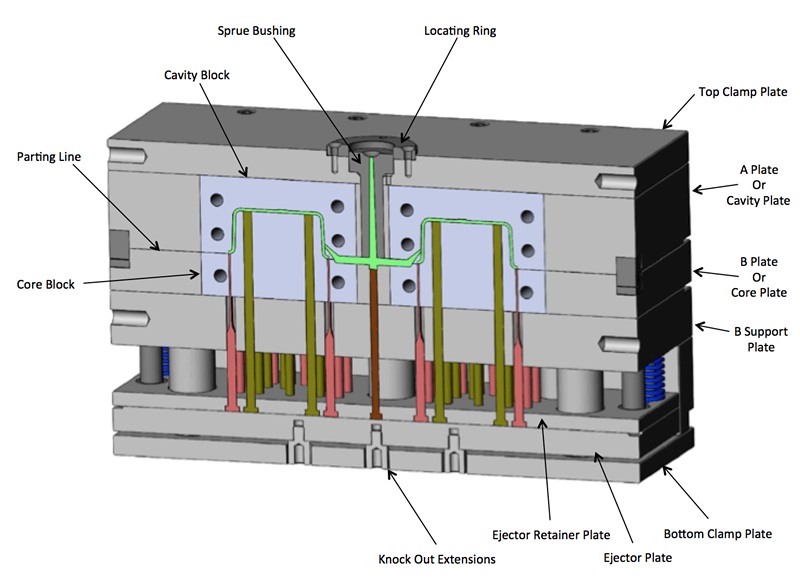
Hot Runner Injection Mold Disadvantages
●You cannot change the plastic material color just as you want it.
●It is not suitable for materials that don’t react well to heat, such as polymers and resins.
●You will need to wait for some time before the plastic materials can cool down during the injection molding process.
Cold Runner Injection Mold Disadvantages
●In most cases, you can’t recycle the waste materials produced by the cold runner molding system.
●It will give you a slower overall production cycle.
●You can only use specific materials for this process, such as resins and polymers.
Is Hot Runner Better than Cold Runner?
Determine whether the hot runner or cold runner system is better, it will depend on your manufacturing needs. For example, with some plastic materials, such as resins and polymers, you can’t use the hot runner system to process them.
These materials will not have a stable form when exposed to the heat generated by the hot runner system. So, you will need to use the cold runner system to process the resin and polymer materials in your production cycles.
Thus, there is no such thing as a better or worse injection molding method between the hot runner and cold runner systems, as they both have their own use.
Choosing between These 2 Runners in Manufacturing
Manufacturers, they will choose to use the hot runner injection mold if they need to process large production volumes at the fastest production cycles. They will also use the hot runner molding system for most plastic materials, as these materials are easier to manage during the molding and die cast metal process.
However, manufacturers will still use the cold runner system, although it is slower than the hot runner system if they need to process resins and polymers in their production cycles. Also, the cold runner system allows them to change the colors of the materials at will, making it easier for them to create variations of their products.
All that matters is the production needs of each manufacturer, the materials they are using, and the production schedule they are planning. They will match these aspects and use the runner system that can accommodate their production plan in the best way.
In order to have a significantly comparison, we have the table below:
| Comparison Factor | Hot Runner Mold | Cold Runner Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Runner temperature | Molten plastic stays heated inside the mold | Plastic solidifies in the runner after each cycle |
| Mold start-up time | Requires controlled warm-up before production | Can start molding immediately |
| Part weight consistency | Very stable shot-to-shot part weight | Slight weight variation possible |
| Gate vestige size | Small, clean gate marks | Larger gate marks, often require trimming |
| Post-processing needs | Minimal or none | Degating and runner removal required |
| Energy usage pattern | Higher energy per hour, lower per part | Lower energy per hour, higher per part |
| Maintenance complexity | Requires skilled maintenance and diagnostics | Simple maintenance and easy repair |
| Downtime risk | Longer downtime if heating system fails | Shorter downtime due to simple design |
| Design flexibility | Flexible gate placement for complex parts | Gate location limited by runner layout |
| Multi-cavity balance | Excellent cavity-to-cavity flow balance | More challenging to balance |
| Best production volume | Medium to very high volumes | Prototype to low-volume production |
| Product life-cycle fit | Mature, stable designs | Early-stage or frequently changing designs |
| Long-term cost trend | Cost per part decreases as volume increases | Cost per part increases with material waste |
Conclusion
Hot runners and cold runners are an important part of any injection molding process. Each runner system has its own pros and cons, which gives the manufacturers the options on which runner system to use depending on the projects or production requests they need to complete. Both the hot and cold runner systems have their own compatibility with certain plastic materials for injection molding, so you can’t just abandon one runner and pick the other one, as you will need to use both runners at some point.
Contact Us – Get the Right Injection Mold Solution
Tooling cost, cycle time, material usage, and long-term part quality are affected by the runner types, so choose between a hot runner and cold runner mold is important. You can base on part design, material, volume, and product life cycle etc. requirements to get the right choice.
At TEAM RAPID, our engineers help you:
- Use the read production data to evaluate hot runner vs cold runner
- Suggest the best gate design, runner layout, and mold structure
- Maximumly reduce material waste, cycle time, and overall mold cost
- Transition smoothly from rapid prototype to mass production
Whether you’re developing a new product or improving an existing mold, we provide practical, cost-effective injection molding solutions for low to high volumes.

Faster doesn’t mean better, while slower also doesn’t mean worse. It’s best for you to pick the right runner system to use, depending on the project requirements you need to fulfill from your clients. TEAM RAPID offers professional injection molding services and rapid prototyping services, contact our team today to get the right runner system for your upcoming tooling projects!
FAQs – Hot Runner vs Cold Runner Injection Molds
1. Which mold type is better for prototypes or low-volume production?
Cold runner molds are better, as they are cheaper to make, simpler, and easier to modify for prototypes and low-volume runs.
2. When should I choose a hot runner mold?
Hot runner molds are ideal for:
- High-volume production
- Parts with tight tolerances
- Products that require consistent part weight
- Minimal post-processing.
3. How do hot runner and cold runner molds affect material usage?
Hot runner molds’ material-efficiency is better than cold runner molds, especially for the high-volume production runs. Cold runner molds produce solidified runners that must be trimmed or recycled, increasing material use.
4. Are hot runner molds more expensive than cold runner molds?
Yes!
- Hot runner molds have higher upfront costs due to heaters and temperature controls, but they reduce per-part cost in high-volume production.
- Cold runner molds are cheaper initially but can be more expensive over time for large runs.
5. Can I switch from cold runner to hot runner later?
Yes, but it often requires a full mold redesign and additional investment. It’s best to decide early based on expected production volume and product lifecycle.




