CNC Prototyping vs. Vacuum Casting: A Complete Rapid Prototyping Comparison
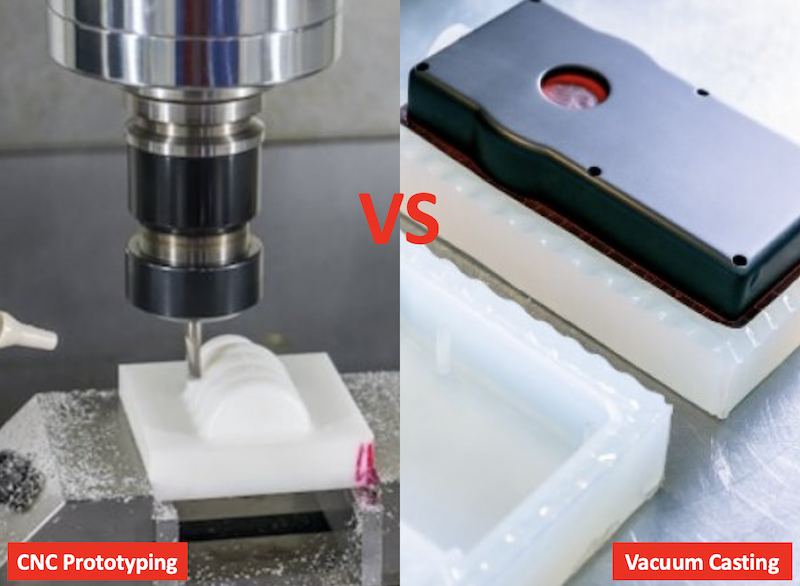

INTRODUCTION
Picking a suitable quick rapid prototyping technique can make or break your product development plan in the competitive accessory manufacturing market of today. Vacuum casting and CNC prototyping are two effective methods that have become industry favorites. Each has unique benefits for turning your ideas into reality, but many manufacturers still struggle to decide which approach to employ when.
Vacuum casting and CNC prototyping are both essential parts of the rapid prototyping toolbox. Before agreeing to costly mass manufacturing, they allow engineers and designers to examine shape, fit, and functionality. The methods taken by these two approaches, yet, could not be more dissimilar. Vacuum casting uses silicone molds to duplicate parts from a master template, whereas CNC machining extracts material from a solid block to produce precise prototypes.
Understanding CNC Prototyping
What is CNC Prototyping?
CNC prototyping is the process of creating prototype parts by removing material from a solid workpiece using computer numerical control machines. A CNC prototype is generated using automated, computer-guided cutting tools that adhere to highly precise computerized instructions, compared to conventional manual machining. The most efficient approach for producing working prototypes that are identical to finished parts for production is subtractive manufacturing (SM).
A 3D CAD model of the part you are seeking is the first step in the process. This design is transformed by engineers into machine-readable code (G-code and M-code) that informs the CNC machine on precise movement, cutting depth, and tool selection. The ability of CNC quick prototyping to deal with real production materials from aluminum and stainless steel to industrial polymers like ABS and polycarbonate makes it particularly helpful.
How CNC Machining Prototyping Works
Rapid CNC prototyping's simple workflow is part of what makes it exquisite. The CNC machining prototyping process proceeds quickly once your CAD file is prepared. Once the workpiece is fastened to the machine bed, the cutting tools start their meticulously coordinated action, removing extra material layer by layer. Common CNC operations include drilling (to create accurate holes), turning (where the workpiece spins across a stationary tool), and milling (where revolving cutters remove material).
The remarkable accuracy that CNC prototyping services offer is one of their main advantages. Modern CNC machines are great for products that need precise fittings or mechanical functionality since they can hold tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm. You may get from digital design to actual prototype in hours or days as opposed to weeks, avoiding the need for pricey molds and time-consuming setup.
Key Advantages of CNC Prototype Creation
The CNC prototype experience has been defined by speed and adaptability. Do you need to alter the design? Just run a different part after making changes to your CAD file. CNC machining prototyping is extremely useful during the development phase when designs change quickly because of its iterative capabilities. Before investing in production tooling, you test actual material qualities, identify problems early, and verify mechanical performance.
Additionally, CNC prototyping provides unparalleled material diversity. CNC machining can handle any accessory that needs the strength of stainless steel, the lightweight qualities of aluminum, or the chemical resistance of specific plastics. This gives you confidence in your design choices because your prototype functions similarly to the actual thing.
Understanding Vacuum Casting
What is Vacuum Casting?
Rapid prototyping is approached quite differently with vacuum casting. This method replicates parts by making a silicone mold from a master pattern and then casting replicas using specialized resins rather than removing material. Imagine creating ice cubes using materials that behave like production plastics with industrial-grade precision.
A master model, usually produced by CNC machining or 3D printing, is the first step in the process. Everything that comes after is modeled after this master. A silicone mold vacuum casting setup is then constructed by a vacuum casting manufacturer based on this master design. Technicians remove the master, carefully cut the mold open (typically in two parts), and create channels for resin pouring and air venting when the silicone has cured.
The Vacuum Casting Process
This is where the magic takes place. A two-part vacuum casting resin, typically polyurethane formulas intended to imitate particular production materials is combined. To get rid of any trapped air bubbles, the combined resin is then degassed in a vacuum chamber. The resin flows via finely crafted gates into the silicone mold under continuous vacuum pressure.
One important function of the vacuum environment is to remove air pockets that could otherwise result in surface flaws or weak places. Even the smallest details from the original master pattern are captured when the liquid resin fills every inch of the vacuum casting mold, including minute intricacies and surface textures that would be practically hard to duplicate in any other way.
The mold opens to expose an almost flawless replica of the master after curing (usually at about 70°C). Every vacuum-cast component preserves the original's surface quality and dimensional correctness. Before detail deterioration necessitates mold replacement, a single silicone mold may normally create 15–25 excellent replicas.
Benefits of Vacuum Cast Parts
The material diversity of vacuum casting makes it especially appealing for the production of accessories. Rubber-soft elastomers (Shore A hardness) and rigid engineering plastics (Shore D hardness) can both be simulated using contemporary vacuum casting resin alternatives. Do you need anything that functions similarly to ABS? For that, there is a resin. Are you looking for the flexibility of polypropylene or the clarity of polycarbonate? Resins with these qualities are stocked by facilities and suppliers in China for vacuum casting.
Vacuum cast parts are perfect for market testing, visual prototypes, and even limited production runs since their surface finish quality is comparable to injection molding. Parts can be painted, chromed, or finished just like production items, and colors can be added straight to the resin. Vacuum casting provides an affordable sweet spot that other techniques find difficult to achieve for projects requiring 10 to 50 identical pieces.
CNC Prototyping vs. Vacuum Casting - Direct Comparison
Knowing the practical distinctions between these two manufacturing techniques becomes essential when choosing between them. Let's compare vacuum casting and CNC prototyping in terms of the most important aspects of your project.
-
Cost Comparison
Depending on the scale of output, each method's economics change significantly. CNC machining usually has a cost advantage for single prototype pieces. Simply load your CAD file and begin cutting; no mold has to be made. You are only paying for the material and machine time.
But when you require between five and fifty identical pieces, vacuum casting becomes significantly more cost-effective. The initial cost of making the silicone mold and master pattern is spread out over several copies. Before needing to be replaced, each vacuum casting mold may manufacture 15 to 25 high-quality pieces. In this sweet spot, vacuum casting is frequently 30–50% less expensive per unit than machining each component separately.
-
Production Speed and Lead Time
Your volume needs are the only factor that determines speed. Do you need a single working prototype by tomorrow? Results are produced more quickly using CNC rapid prototyping. Depending on the intricacy, you can have your prototype the same day or the next day because of modern CNC machines that can create intricate pieces in a matter of hours.
Vacuum casting is superior for small batches. A vacuum casting facility may make several copies at once once the silicone mold and master design are available. While each casting cycle takes time for the resin to cure (usually 8-16 hours depending on the material), the ability to run numerous molds in parallel means you may have 20-30 pieces within a few days. Since each demands specific machine time, CNC manufacturing those same 20–30 items separately would take much longer.
-
Material Options and Properties
This is when the disparities really stand up. Nearly limitless material options are available with CNC prototyping. For a working bracket, do you need stainless steel? For lightweight housing, aluminum? Chemical resistance using high-performance PEEK plastic? They are all handled via CNC machining. Your prototype acts exactly like the finished product since you are using real manufacturing materials.
Although there are many possibilities for vacuum casting resin, they are still restricted to materials based on polyurethane. Many manufacturing plastics, from soft rubber-like elastomers to stiff ABS-like materials, may be simulated using contemporary vacuum casting resin formulas. Even transparent resins that resemble polycarbonate or colored versions that meet your brand's specifications are available. However, it's crucial to realize that they are resin models of production materials rather than the actual materials.
-
Precision and Tolerances
Requirements for tolerance may be a decisive factor. With tolerances of ±0.01mm to ±0.05mm, depending on the shape and material, CNC machining prototype provides remarkable dimensional precision. Because of its accuracy, CNC is perfect for pieces that need to join with other parts, have threaded features, or have precise mechanical fits.
The precision of vacuum casting is usually within ±0.2mm of the master pattern dimensions. This is more than sufficient for many applications, particularly visual prototypes or parts lacking crucial mating surfaces. Vacuum cast items frequently have surface finishes that are on par with or better than CNC machined surfaces, especially for intricate organic forms.
CNC Prototyping vs. Vacuum Casting – Comparison Table
Comparison Factor
CNC Prototyping
Vacuum Casting
Best Production Volume
Single prototypes or very low quantities (1–3 pcs)
Small batch production (5–50 pcs)
Cost Efficiency
More cost-effective for one-off parts since no mold is required
Lower cost per unit for small batches due to shared mold cost
Upfront Tooling Cost
None – parts are machined directly from the CAD file
Requires a master pattern and silicone mold
Per-Unit Cost Trend
Cost remains high as quantity increases
Becomes 30–50% cheaper per unit in the 5–50 piece range
Typical Mold Life
Not applicable
One silicone mold produces ~15–25 high-quality parts
Lead Time for First Part
Same day or next day, depending on complexity
Longer initial setup due to mold creation
Production Speed
Very fast for single parts; machining completed in hours
Efficient for small batches with multiple castings run in parallel
Batch Production Time
Slower for multiple identical parts since each part is machined separately
20–30 parts can be produced within a few days
Curing / Processing Time
No curing required
Resin curing takes approximately 8–16 hours per cycle
Ideal Use Case
Functional testing, precision prototypes, urgent turnaround
Design validation, appearance models, low-volume production
When to Choose CNC Machining Prototyping
You could save time, money, and inconvenience by knowing when to use CNC prototyping services. In these situations, a CNC machining prototype is the ideal choice.
When you require functioning prototypes created from real production materials, go with CNC prototyping. Testing with the actual thing is essential if your finished product will be made of aluminum, stainless steel, or engineering-grade polymers like PTFE or PEEK. You can be confident that your design will function as intended since the mechanical qualities, thermal characteristics, and structural integrity of CNC-machined parts match what you'll get in production.
Rapid CNC prototyping is also indicated by high accuracy requirements. CNC machining provides the necessary precision when tolerances of less than ±0.2mm are important for your application. This makes it essential for applications where dimensional precision directly affects functioning, assemblies that need to fit precisely, or parts that must communicate with other components.
CNC is also preferred for single prototypes or extremely small volumes (one to three pieces). You can get from a CAD file to a real part very quickly without having to invest in any tools. When you're refining geometry, testing various combinations, or verifying mechanical performance throughout iterative design phases, this speed becomes crucial. Product development is greatly accelerated when you may change your design and create a new prototype in a matter of hours.
CNC machining is often used for prototype development in industries including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. These industries require the authenticity, accuracy, and dependability of materials that only CNC prototyping can offer. CNC-machined components made from production materials are the clear option when your prototype must endure stress testing, heat cycling, or regulatory inspection.
Lastly, CNC machining is a logical solution if your design calls for precise holes, threaded inserts, or stringent geometric tolerances that would be difficult to accomplish by casting.
When to Choose Vacuum Casting
Compared to CNC machining, vacuum casting excels in quite different situations. Optimizing quality and cost-effectiveness may be achieved by knowing when to use this procedure.
Small manufacturing runs of five to fifty identical pieces are ideal for vacuum casting. Vacuum casting offers outstanding value once your design has been verified and you require several copies for market testing, client presentations, trade exhibitions, or small production batches. When compared to machining each component separately, the cost per item decreases dramatically while preserving production-quality functioning and appearance.
Appearance models and visual prototypes are also excellent uses. Vacuum casting resin alternatives are just as versatile as injection molding when it comes to aesthetic appeal, such as color matching, surface roughness, and transparent characteristics. When making prototypes for design reviews, photography, or client feedback sessions, accessory makers especially profit from this capabilities.
Vacuum casting is often preferred for complex organic structures with undercuts, flowing curves, or fine surface details. The flexible silicone mold vacuum casting method captures complex geometries that would need costly multi-axis machining equipment, but CNC machining excels at geometric precision. This makes it ideal for parts with ornamental textures, curved housings, and ergonomic grips.
The reduced tooling costs of vacuum casting are advantageous for applications on a tight budget. Vacuum cast parts only require silicone molds and a master template, in contrast to injection molding, which requires costly steel molds. Because you need to evaluate form and fit before committing to mass production tooling, this makes it cost-effective for pre-production validation.
The inexpensive pricing offered by vacuum casting facilities in places like China further strengthens the economic benefit for small quantities. This method produces excellent results at a fraction of injection molding expenses when your schedule permits the initial master pattern generation and mold production (usually 5-7 days) and your material needs match available vacuum casting resin possibilities.
Applications in Accessories Manufacturing
Rapid prototyping is crucial since the accessory manufacturing sector has particular difficulties. Both vacuum casting and CNC prototyping are essential to taking things from idea to market, whether you're creating jewelry, fashion accessories, electrical device accessories, or car add-ons.
The capacity of vacuum casting to produce intricate, eye-catching prototypes greatly benefits fashion and jewelry accessories. Before committing to production tooling, designers may test a variety of color options, textures, and finishes. A vacuum casting foundry can effectively generate 15–25 identical parts from a single mold, which makes it possible to produce samples for market testing, buyer presentations, and trade shows, all crucial tasks in an industry where visual appeal influences purchase choices.
Vacuum Cast Parts in Functional Accessory Design
Combining the two approaches is quite helpful for practical accessories like phone covers, laptop stands, or car organizers. For goods that must endure frequent usage, exact fits with other devices, and occasionally difficult climatic conditions, CNC machining prototype verifies mechanical performance. Testing prototypes constructed from real production materials, such as nylon, polycarbonate, or aluminum, guarantees that your design functions as intended.
Vacuum cast components, on the other hand, are excellent for creating transparent windows, ornamental coverings, and softer-touch components. Manufacturers of electronic accessories frequently combine the two approaches: Vacuum casting delivers the aesthetically pleasing and tactile components that customers directly engage with, while CNC prototyping produces exact housing components with strict tolerances for inside circuitry.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Partner
Vacuum Casting Mold Quality and Silicone Mold Vacuum Casting Expertise
Any vacuum casting project's success depends on the quality of the mold. Every detail of your master design is captured by a well-built vacuum casting mold, which yields consistent results across several casting cycles. Specialized expertise is needed for the silicone mold vacuum casting process, from choosing the ideal silicone hardness to creating the best separating lines and gate placements.
Look for establishments that have proficiency in both silicone mold manufacture and master pattern generation when assessing manufacturing partners. The top vacuum casting facilities make investments in premium silicone materials that are resistant to ripping and preserve dimensional stability over the course of the mold's life. Your vacuum cast parts will be consistent from the first casting to the last thanks to this attention to detail.
Vacuum Casting China: Global Manufacturing Considerations
Your prototyping expenses and schedule may be greatly impacted by your geographic location. For many Western businesses, vacuum casting operations in China have become competitive choices because they provide cost benefits without sacrificing quality requirements. From initial design advice to final finishing, Chinese vacuum casting firms frequently offer full services at prices that make small-batch manufacturing economically feasible.
But go beyond per-part pricing and take into account the whole cost equation. Longer lead times for modifications, complicated communication, and international shipment all play a role in the choice. Despite increased per-unit costs, local CNC prototyping services may be advantageous for projects needing close collaboration throughout the development process. Offshore vacuum casting facilities can provide significant savings for verified designs that require 20–50 production-quality samples.
CONCLUSION
Selecting between vacuum casting and CNC prototyping is more about matching the appropriate technique to your particular project requirements than it is about identifying a generally "better" approach. While both methods are excellent at quick prototyping, they fulfill quite different purposes within the product development cycle.
When you want material authenticity, precise tolerances, or rapid turnaround on single prototypes, CNC prototyping services can help. It is the preferred option for mechanical validation, functional testing, and applications where accuracy is crucial. CNC machining prototype is essential for thorough engineering validation since it allows one to work with real production materials.
Contact Us & Get Expert Guidance
Are you looking for CNC prototyping or vacuum casting for your project? Our experienced engineers are here to help you evaluate cost, lead time, materials, and production volume—so you can move forward with confidence. TEAM RAPID provides both CNC rapid prototyping and vacuum casting services, allowing us to recommend the best solution based purely on your design and project goals—not limitations.
- Upload your CAD files today to receive a fast, free quote and professional manufacturability feedback.
- Need technical advice? Contact our team to discuss your prototype or low-volume production requirements.
- Tight deadline or complex geometry? We specialize in rapid turnaround and precision manufacturing.
Get in touch now and turn your design into high-quality parts—faster, smarter, and cost-effectively.
CNC Prototyping vs. Vacuum Casting – FAQs
FAQ Question
Short Answer
What is the main difference between CNC prototyping and vacuum casting?
CNC prototyping machines parts directly from solid materials, while vacuum casting produces parts by pouring resin into silicone molds. CNC is best for single, high-precision parts; vacuum casting is ideal for small batches.
Which process is more cost-effective for my project?
CNC prototyping is more economical for one-off parts with no tooling cost. Vacuum casting becomes more cost-effective for 5–50 identical parts due to lower per-unit costs.
When should I choose vacuum casting instead of CNC machining?
Choose vacuum casting when you need multiple identical parts, consistent surface finish, or appearance models for design validation or pre-production testing.
How fast can I get parts using CNC prototyping or vacuum casting?
CNC prototyping can deliver parts in the same day or next day. Vacuum casting takes longer initially but can produce 20–30 parts within a few days once the mold is ready.
How do I choose the right process for my project?
The best choice depends on part quantity, budget, lead time, material needs, and end use. Our engineers can review your design and recommend the most efficient solution.