Injection Molding Tolerances and How to Optimize Them
Injection molding is a manufacturing method which is ideal for mass production. Plastic molding process involves injecting molten thermoplastics or thermosets into metal molds. When the material has cooled, the parts are being ejected. This process repeats. Injection molding process allows manufacturer to produce identical parts in high volume quickly and economically.
What is Injection Molding Tolerances
Material shrinkage which happens naturally, and slight variations between can be expected. It is important to set a precise range of acceptable variation which will allow the part to perform ass desired. These acceptable range of variation or injection molding tolerances are important for large parts and those assembled from multiple parts. If the variation between parts is not kept within acceptable limits for standard injection molding tolerances, they can not fit together. And the part will not perform as desired.
Injection molds are CNC machined to tolerances of ±.005 inches. Injection molding tight tolerance refers to ±.002 inches in variation. Very tight tolerance refers to ±.001 inches. Compared with injection molding parts with tight tolerances, parts with normal tolerances are less expensive. So, determining the optimal tolerances for injection molded parts is important for parts with high quality at an affordable way.
Injection molding tolerance is important
Specify injection molding tolerances correctly is important to make sure the final parts can fit together during assembly. Controlling injection molding tolerance can ensure high quality by design for manufacturing principles, material selecting, tool design and process control.
There is always variation when it comes to producing parts. It is important to define an acceptable range of variation allows the part to perform as desired. This is more and more important when several parts are assembled. For example, if two flat parts have to be bolted together, the locational tolerances of holes on each part have to allow for full range of possibilities. A part has minimum tolerance and the other has maximum tolerance, they must fit together in assembly process. This sounds simple, but when several parts need to be assembled a part can cause the whole assemble to be not functional. Tolerance stack and statistical analysis can be sued to optimize injection molding tolerance of several assemblies.
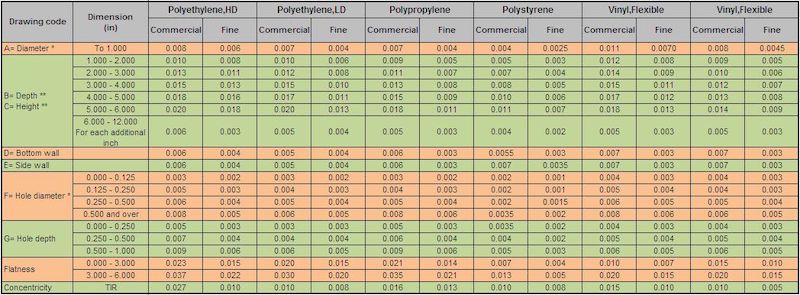
How to Define the Tolerance Class for My Injection Mold Part
Without a corrected tolerance class, we can’t ensure injection molded part functional performance, consistent quality, and reasonable production cost.Tolerance classes make everything clearly and easily to communicate expectations between designers and mold makers, it groups dimensions by accuracy level.Rather than applying tight tolerances everywhere, selecting the appropriate tolerance class allows manufacturers to control variation where it matters most.
Tolerance Class
Typical Application
Part Size / Feature Type
Material Suitability
Cost & Complexity Impact
General (Standard)
Cosmetic parts, covers, housings, non-functional features
Large dimensions, wall thickness, external surfaces
Most plastics, including PP, ABS, PE
Lowest tooling and production cost
Precision
Assembly features, snap fits, alignment surfaces
Medium-size features, mating dimensions
ABS, PC, PS, glass-filled materials
Moderate tooling accuracy and process control
High-Precision (Critical)
Sealing surfaces, moving interfaces, bearing areas
Small, critical dimensions only
Dimensionally stable plastics (ABS, PC, PMMA)
Higher tooling cost, strict process control
Ultra-Precision (Special Cases)
Medical, optical, safety-critical components
Very small, tightly controlled features
Limited materials with proven stability
Highest cost, may require secondary machining
How to optimize injection molding tolerances
1. Design
Considering tolerance early in the design stage is a key to avoid costly and time-costing redesigns in later production. To minimize the potential of warping and misalignments, designers have to ensure they are adhering DFM best practices. DFM stands for design for manufacturability. It is a principle that designed parts will specific methods of manufacturing. And the manufacturing method should inform factors like wall thickness, angles, and design features. To prevent uneven shrink rate, it is important to maintain uniform wall thickness. Design features, for example, support ribs are efficient and effective in offering strength than increasing wall thickness. Draft angles are important to ensure that the parts eject easily from the mold without warping or suffering scrape. Appropriate angles vary according to the part design and surface finish. 1.5-2.0 degrees of draft is a safe minimum for many injection molded parts.
2. Materials
Injection molding tolerances are impacted by materials. So, materials selection is as important and part design. There are a wide range of plastic available for injection molding process. Different materials have different shrinkage rates. This must be factored in to material selection and the mold design. If the parts have components which made from more than one material, manufacturers need to consider the different shrink rates to ensure each component fit together as desired. So, a clear understanding of various injection molding material is important to ensure consistent injection molding tolerances.
3. Tooling consideration
Mold tools are designed to be slightly oversized. The first important things need to determine is the materials being used. Well-designed tools in important to ensure that parts cool and adhere to high injection molding tolerance standards. To maintain tight tolerance, mold tooling has to offer consistent, repeatable heating and cooling between shots. Bad or inconsistent cooling will lead to deviation from tolerance requirement. Engineers can track and adjust production variations to ensure correct pressure, heating and cooling in injection process by monitoring injection molding pressure, resin viscosity and time. An ideal location for the gate helps to avoid uneven fills and minimize incorrect shrinkage and warping. Complex injection molding parts need more than one gate to make sure fill distribution and correct cooling. The tolerances of the tooling are tightly controlled. This is also an important factor that manufacturers have to check.
4. Repeatable process controls
There are a number of variables involved during manufacturing processes. They will affect the part quality. Repeatable process controls are the ways to correct variable. Pressure and temperature in the mold tooling is important in developing robust process controls because they offer feedback on parameters. Manufacturers can make quick modification if any unacceptable variation. When variables are controlled, the mold tooling is able to produce parts with precise injection molding tolerances and minimal variation.

Standardizing factors, such as temperature, injection pressures, and holding time enables manufacturers to refine production processes to achieve consistent results. Plastic has thermal expansion coefficient. They are changing in size as the temperature changes. Injection molded parts with tight tolerance need to be measured under consistent temperature to make sure dimension and performance are consistent.
Optimize injection molding tolerances with TEAM RAPID
Injection molding is an incredibly versatile manufacturing process to produce consistent and durable parts. Some degree of variation can not be avoided during manufacturing, but ensuring deviations are kept within acceptable range is important for manufacturing part with high performing, dimensionally consistent. Reliable, repeatable processes, mold tooling with high quality and good part design for manufacturing are keys to ensure accuracy and consistent part quality. Working with a professional injection molding manufacturer like TEAM RAPID is a great way to make sure that part designs are optimized for production and will adhere to tight dimension tolerances. We will ensure that customers’ investment into the tooling is as risk-free ad possible. At TEAM RAPID, our team have experiences to handle each project. We commit to deliver support from design and prototyping to production. We take on each project at speed and ensure to offer the highest quality standard. Our engineers are happy to offer design for manufacturability feedback and advices before getting the projects underway. To learn more about injection molding tolerances, contact us today for a rapid manufacturing quote.
FAQs – Injection Molding Tolerances
1. Why can’t set tight tolerances everywhere in injection molded parts?
As many factors affect the part’s accuracy. Varies types of plastic material, part thickness, and mold temperature can behavior differ in shrink and deform during cooling.Applying tight tolerances to all dimensions increases tooling complexity and expense, meanwhile, it may still result in inconsistent parts. Selective tolerancing is the most reliable and cost-effective approach.
2. How does material selection affect tolerance capability?
Different plastics behave differently during molding.
- Amorphous plastics such as ABS and PC offer better dimensional stability.
- while semi-crystalline materials like PP and nylon experience higher shrinkage.
Choosing the right material early helps define realistic tolerance classes.
3. When should use the high-precision tolerances?
When dimensions affected part function, such as sealing surfaces, snap-fit features, or moving interfaces, high-precision tolerances should be used.Applying high-precision tolerances to non-functional features increases cost without improving performance.
4. Are tighter tolerances always more expensive?
Typically, yes. Tighter tolerances require higher mold machining accuracy, stricter process control, longer setup time, and more inspection. The goal should be to define tolerances that areas tight as necessary, not as tight as possible.